JS-1 Design
Peptides are involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes and play a very important role in modulating various cell functions.
A notable example is Copaxone. Copaxone which is a synthetic peptide polymer composed of four kinds of amino acids, is a commercial drug for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Though peptides exhibited many advantages, there are still some disadvantages needed to be addressed for their utilization as drugs (Table. C-1) [1].
We determined to design a peptide drug which not only possesses the advantages that come with it, but could also overcome some of the disadvantages. To put our idea into practice, we modified the structure of peptides and ultimately, our peptide-based drug--"JS-1", successfully overcomes some of the disadvantages including poor metabolic stability, poor membrane permeability, and low solubility.
Table. C-1 :The advantages and disadvantages of peptide-based drugs.
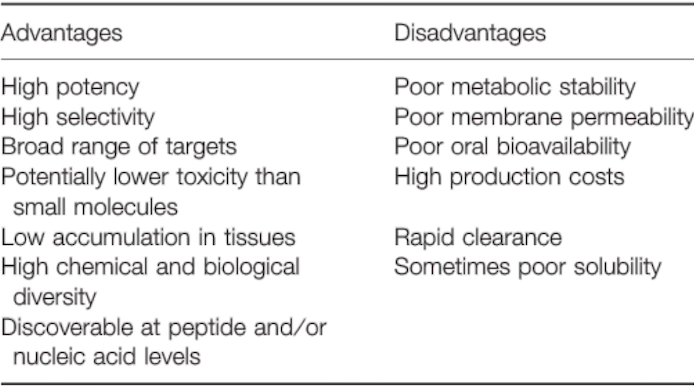
Reference: Chem Biol Drug Des 2013; 81: 136–147.
- The steps of our drug development are:
- (1)Molecular design of peptides with the aid of computer simulation to find the potential hit exhibiting good inhibition of HuR;
- (2)Synthesis of the peptides conjugated with a hydrophilic polymer, and characterization of the nanoparticles assembled by the peptide-based polymers as the delivery vehicles;
- (3)Evaluation of the biochemical properties of the peptides in the delivery vehicles using in vitro cell culture;
- (4)Evaluation of the HuR inhibition of the peptides in the delivery vehicles by scoring the disease symptom in a mice model;
- Chem Biol Drug Des 2013; 81: 136–147.
- Wang, S. H.; Wu, Y. T.; Kuo, S. C.; Yu, J. J Chem Inf Model 2013, 53, (8), 2181-95.
- Moustakas, D. T.; Lang, P. T.; Pegg, S.; Pettersen, E.; Kuntz, I. D.; Brooijmans, N.; Rizzo, R. C. J. Comput Aided Mol Des 2006, 20, (10-11), 601-19.
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW., Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States., J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Mar;70(3):512-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.013. Epub 2014 Jan 2.
- Correia, B.; Torres, T. Acta Biomed 2015, 86, (2), 121-9.
- Ueyama A, Yamamoto M, Tsujii K, Furue Y, Imura C, Shichijo M, Yasui K., Mechanism of pathogenesis of imiquimod-induced skin inflammation in the mouse: a role for interferon-alpha in dendritic cell activation by imiquimod., J Dermatol. 2014 Feb;41(2):135-43. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12367. Epub 2014 Jan 3.
- http://accelrys.com/products/collaborative-science/biovia-discovery-studio/
(1) Design
In molecular design, we adopted the "HotLig" for preliminary analysis and “Discovery Studio” modeling method for theoretical verification [2]. These methods was reported to have satisfactory predictive simulation for binding affinities by calculation of intermolecular forces such as H-bonds, ion-pairs, metal-coordination and hydrophobic effects. With the computer software (Dock 5.1 / Hot-Lig) [3], we can evaluate the candidate molecules, compare them with the existing HuR protein inhibitors, and isolate the selected one with predicted higher binding capacity into further development, thereby saving costs and optimizing the modification of structure.
Before using HotLig, we first modified the peptides with functional groups to protect them from easy degradation. Their building blocks are natural alpha- amino acids including lysine, glutamate, aspartate, phenylalanine, tyrosine, threonine, cysteine, tryptophan, and etc.
After modeling analysis, modified oligoglutamate* was predicted to have the best interaction at the RNA binding site of HuR (Figure. C-1.).
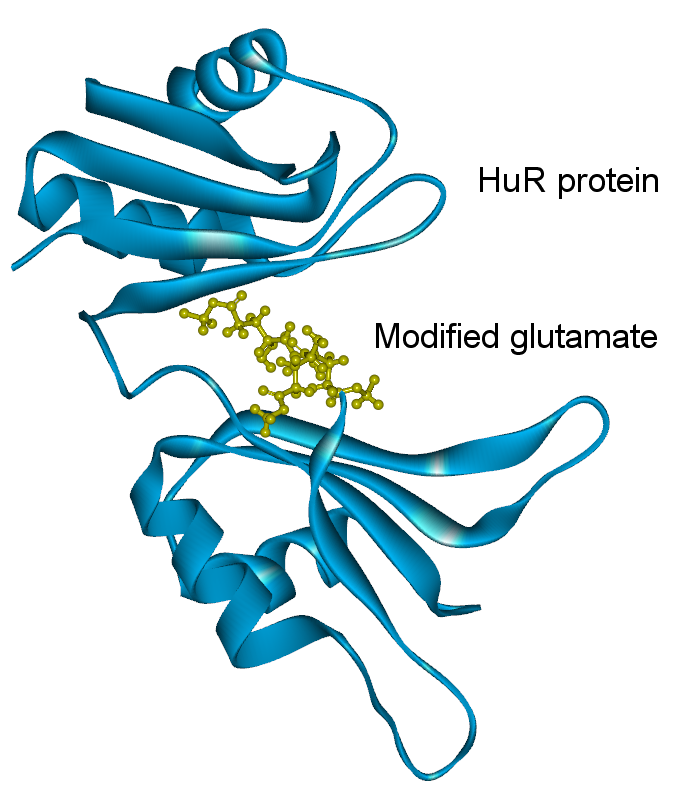 Figure. C-1. Modified glutamate*.
Figure. C-1. Modified glutamate*.
*patent confidentiality
Meanwhile, we use the software "Discovery studio" for double modeling check. The software can verify the best binding sites of the candidate molecules to HuR proteins as well as the most possible binding mode, and presents it with 3D chemical structures [4] (See Simulation for details).
(2) Synthesis and Analysis
Afterwards, we adopted the common “Ring-Opening Polymerization” method [7] to synthesize this peptide-based polymer, which was named JS1, using polyethylene glycol with an amino end group as the initiator, and then it assembled to form nanoparticles which can be easily uptaken by cells (See Experiment 4- In vitro for details). We first confirmed that JS-1 was delivered into cells as predicted by using bio-labeling fluorescent dyes, and then evaluated the actual therapeutic effects on mice models of diseases.
(3) Model: Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. On the lesioned skin region, erythema and scales can be easily noticed and severely undermine the patients’ quality of life [5]. Psoriasis is a common disease in the US with the prevalence of the adults over 20 y/o reaching 3.2% [4]. We attempted to utilize this designed JS-1 to treat psoriasis.
We employed "Imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis model" in mice as an simulation of the psoriasis pathology in human. We smeared IMQ on the skin of mice to induce psoriasis pathological symptoms. After receiving messages from TLR7, dendritic cells secreted cytokines including IFN- α, IL-23, IL-6, TNF- α. These cytokines would stimulate T-cell and cause immune response [6]. When we applied JS-1, the peptide-based nanoparticle vehicle, to lesioned region, the results showed that it could effectively treat the psoriasis symptoms (See Experiment-In vivo) considering the three severity ind ice f psoriasis: erythema, thickness, and scaling.
The success on the mice model lays the foundation for future therapeutic development. We expect that there will be better treatments for frail patients who have suffered from chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer.
Reference: